Angas Tutoring
STEM Education
Your Javascript is disabled. Some navigation on this site will not work without Javascript. Please enable Javascript in your browser to enjoy all features of this site.
Home About Us Subjects Tutored FAQ Testimonials Ponder This Contact Us
Algebra Challenge Geometry Challenge Calculus Challenge Physics I Challenge

All science is either physics or stamp collecting.
Lord Kelvin
Lord Kelvin
Physics I - Classical Mechanics
1. Difficulty: Beginner 
A ball is thrown directly downward, with an initial speed of 8.00 m/s, from a height of 30.0 m. After what time interval does the ball strike the ground?
A ball is thrown directly downward, with an initial speed of 8.00 m/s, from a height of 30.0 m. After what time interval does the ball strike the ground?
1.79 s
2. Difficulty: Beginner 
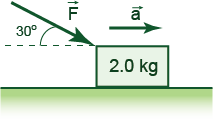
A block is pushed along a frictionless surface as shown in the Figure.
If a = 2.5 m/s2, what is the magnitude of the applied force?
A block is pushed along a frictionless surface as shown in the Figure.
If a = 2.5 m/s2, what is the magnitude of the applied force?
5.8 N
3. Difficulty: Beginner 
A 70-kg man on ice skates pushes a 40-kg boy with a force of 100 N. What is the magnitude of the force exerted by the boy on the man?
A 70-kg man on ice skates pushes a 40-kg boy with a force of 100 N. What is the magnitude of the force exerted by the boy on the man?
100 N
4. Difficulty: Beginner 
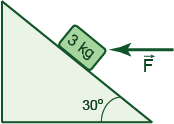
A block is pushed up a frictionless incline by an applied horizontal force as shown in the Figure. If F = 25 N what is the magnitude of the resulting acceleration of the block?
A block is pushed up a frictionless incline by an applied horizontal force as shown in the Figure. If F = 25 N what is the magnitude of the resulting acceleration of the block?
2.3 m/s2
5. Difficulty: Beginner 
(a) What is the angular speed of the second hand of a clock?
(b) What is the direction of the angular velocity vector as you view a clock hanging on a vertical wall?
(c) What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the second hand?
(a) What is the angular speed of the second hand of a clock?
(b) What is the direction of the angular velocity vector as you view a clock hanging on a vertical wall?
(c) What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the second hand?
(a)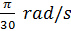 rad/s
rad/s
(b) into the wall
(c) 0
(b) into the wall
(c) 0
6. Difficulty: Beginner 
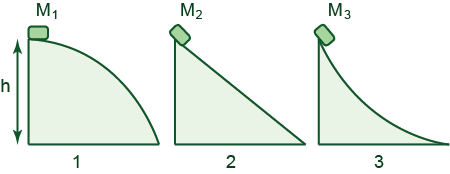
Three objects with different masses are released from rest to slide down frictionless ramps of identical heights but different profiles (see the Figure).
(a) Rank the objects by their final speeds.
(b) Rank the objects by the time it takes them to reach the bottom of their ramps.
Three objects with different masses are released from rest to slide down frictionless ramps of identical heights but different profiles (see the Figure).
(a) Rank the objects by their final speeds.
(b) Rank the objects by the time it takes them to reach the bottom of their ramps.
(a) V1 = V2 = V3
(b) t3 < t2 < t1
(b) t3 < t2 < t1
7. Difficulty: Beginner 
A block is given an initial velocity of 5.00 m/s up a frictionless plane inclining 20°. How far up the incline does the block slide before coming to rest?
A block is given an initial velocity of 5.00 m/s up a frictionless plane inclining 20°. How far up the incline does the block slide before coming to rest?
3.73 m
8. Difficulty: Easy 
A 60-kg man weights himself by standing on a scale in an elevator. What does the scale read when
(a) the elevator is descending at a constant rate of 20 m/s;
(b) the elevator is descending at 20 m/s and gaining speed at a rate of 2 m/s2;
(c) elevator is ascending at 20 m/s but its speed is decreasing by 2 m/s each second.
A 60-kg man weights himself by standing on a scale in an elevator. What does the scale read when
(a) the elevator is descending at a constant rate of 20 m/s;
(b) the elevator is descending at 20 m/s and gaining speed at a rate of 2 m/s2;
(c) elevator is ascending at 20 m/s but its speed is decreasing by 2 m/s each second.
(a) 588.6 N
(b) 468.6 N
(c) 468.6 N
(b) 468.6 N
(c) 468.6 N
9. Difficulty: Easy 
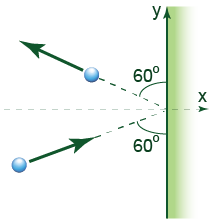
A 3.00-kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 10.0 m/s at an angle of 60° with the surface. It bounces off with the same speed and angle. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.200 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball?
A 3.00-kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 10.0 m/s at an angle of 60° with the surface. It bounces off with the same speed and angle. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.200 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball?
260 N normal to the wall
10. Difficulty: Easy 
The distance between two telephone poles is 50.0 meters. When a 1.00 kg bird lands on the telephone wire midway between the poles, the wire sags 0.200 m. Find the tension in the wire. Ignore the weight of the wire.
The distance between two telephone poles is 50.0 meters. When a 1.00 kg bird lands on the telephone wire midway between the poles, the wire sags 0.200 m. Find the tension in the wire. Ignore the weight of the wire.
613 N
11. Difficulty: Easy 
A moving 2.5 kg block collides with a horizontal spring whose spring constant is 320 N/m. The block compresses the spring a maximum distance of 7.5 cm from its rest position. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.25.
(a) How much work is done by the spring in bringing the block to rest?
(b) How much mechanical energy is dissipated by the force of friction while the block is being brought to rest by the spring?
(c) What was the speed of the block when it hit the spring?
A moving 2.5 kg block collides with a horizontal spring whose spring constant is 320 N/m. The block compresses the spring a maximum distance of 7.5 cm from its rest position. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.25.
(a) How much work is done by the spring in bringing the block to rest?
(b) How much mechanical energy is dissipated by the force of friction while the block is being brought to rest by the spring?
(c) What was the speed of the block when it hit the spring?
(a) -0.90 J
(b) 0.46 J
(c) 1.0 m/s
(b) 0.46 J
(c) 1.0 m/s

12. Difficulty: Easy 
A freely falling object requires 1.50 seconds to travel the last 30.0 m before it hits the ground. From what height above the ground did it fall?
A freely falling object requires 1.50 seconds to travel the last 30.0 m before it hits the ground. From what height above the ground did it fall?
38.2 m
13. Difficulty: Easy 
A 4.0 kg block starts up a 30° incline with 128 J of kinetic energy. How far will it slide up the plane if the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30?
A 4.0 kg block starts up a 30° incline with 128 J of kinetic energy. How far will it slide up the plane if the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30?
4.3 m
14. Difficulty: Easy 
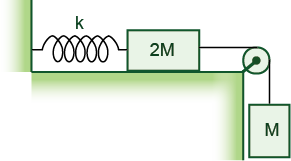
The blocks shown in the Figure are released from rest with the spring unstretched. The horizontal surface is frictionless. If k = 400 N/m and M = 4.5 kg, what is the maximum extension of the spring?
The blocks shown in the Figure are released from rest with the spring unstretched. The horizontal surface is frictionless. If k = 400 N/m and M = 4.5 kg, what is the maximum extension of the spring?
22 cm
15. Difficulty: Easy 
A projectile is launched from the level ground in such a way that the maximum height of its flight is equal to its horizontal range. At what angle above the horizontal is the projectile launched? Would your answer be different on a different planet?
A projectile is launched from the level ground in such a way that the maximum height of its flight is equal to its horizontal range. At what angle above the horizontal is the projectile launched? Would your answer be different on a different planet?
76 degrees
The answer would be the same on a different planet
The answer would be the same on a different planet
16. Difficulty: Medium 
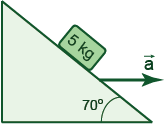
A 5-kg block rests on a frictionless wedge that inclines 70° and has acceleration a directed to the right such that the mass remains stationary relative to the wedge (see the Figure).
(a) Find the magnitude of the acceleration a;
(b)What would happen if the wedge were given a greater acceleration?
A 5-kg block rests on a frictionless wedge that inclines 70° and has acceleration a directed to the right such that the mass remains stationary relative to the wedge (see the Figure).
(a) Find the magnitude of the acceleration a;
(b)What would happen if the wedge were given a greater acceleration?
(a) 27 m/s2
(b) The block would move up the wedge.
(b) The block would move up the wedge.
17. Difficulty: Medium (Calculus required) 
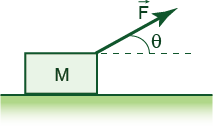
A box of mass 10kg rests on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction is 0.5. A force F is applied at an angle theta as shown in the Figure.
(a) What is the minimal magnitude of the force F that is needed to move the box?
(b) At what angle the force with magnitude found in part (a) should be applied to move the box?
A box of mass 10kg rests on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction is 0.5. A force F is applied at an angle theta as shown in the Figure.
(a) What is the minimal magnitude of the force F that is needed to move the box?
(b) At what angle the force with magnitude found in part (a) should be applied to move the box?
(a) 43.9 N
(b) arctan(0.5)=26.6°
(b) arctan(0.5)=26.6°
18. Difficulty: Medium 
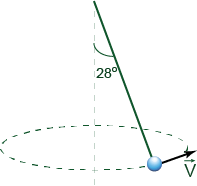
A 3.0-kg ball attached by a 2.0 m string to a vertical axis is rotated about that axis and moves in a horizontal circle. The angle between the string and the axis is 28°. What is the speed of the ball?
A 3.0-kg ball attached by a 2.0 m string to a vertical axis is rotated about that axis and moves in a horizontal circle. The angle between the string and the axis is 28°. What is the speed of the ball?
2.2 m/s
19. Difficulty: Medium 
Blocks of mass M and 2M are connected by a string (see the Figure). Find the tension in the connecting string.
Blocks of mass M and 2M are connected by a string (see the Figure). Find the tension in the connecting string.
30 N

20. Difficulty: Hard 
You are in charge of designing a fountain. The vertical exit speed of the water V0w emitted through a nozzle of the fountain in an upward direction is varied in time and is controlled by a computer. The fountain operates in cycles: in each cycle, a "Water Column" of height h is produced. Then it falls and a new cycle begins. You need to program a computer (fountain) such that the "Water Column" makes a maximal splash when it falls. In other words, what should be a V0w as a function of time for all water emitted during one cycle to reach the ground at the same time? Neglect air resistance.
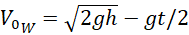
You are in charge of designing a fountain. The vertical exit speed of the water V0w emitted through a nozzle of the fountain in an upward direction is varied in time and is controlled by a computer. The fountain operates in cycles: in each cycle, a "Water Column" of height h is produced. Then it falls and a new cycle begins. You need to program a computer (fountain) such that the "Water Column" makes a maximal splash when it falls. In other words, what should be a V0w as a function of time for all water emitted during one cycle to reach the ground at the same time? Neglect air resistance.
21. Difficulty: Hard 
A clown is juggling several balls simultaneously. The mass of each ball is m=200g. Students use a videotape to determine that it takes the clown a time Δt (Δt = 0.5s) to cycle each ball through his hands (including catching, transferring, and throwing) and to be ready to catch the next ball. An assistant is helping the clown to add more balls to those being handled by the clown. What is the maximal number of balls that the clown may juggle simultaneously if he can provide an average power of up to Pmax=100Watt throwing those balls (the clown spends some energy throwing those balls. Assume he neither spends nor receives any energy when he catches and transfers them).
A clown is juggling several balls simultaneously. The mass of each ball is m=200g. Students use a videotape to determine that it takes the clown a time Δt (Δt = 0.5s) to cycle each ball through his hands (including catching, transferring, and throwing) and to be ready to catch the next ball. An assistant is helping the clown to add more balls to those being handled by the clown. What is the maximal number of balls that the clown may juggle simultaneously if he can provide an average power of up to Pmax=100Watt throwing those balls (the clown spends some energy throwing those balls. Assume he neither spends nor receives any energy when he catches and transfers them).
10


22. Difficulty: Hard 
Find the center of mass of the uniform plate shown in the figure. Assume you have a ruler without labels such that you may draw straight lines but you may NOT measure anything.
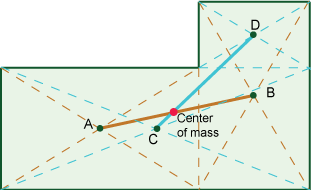
Find the center of mass of the uniform plate shown in the figure. Assume you have a ruler without labels such that you may draw straight lines but you may NOT measure anything.

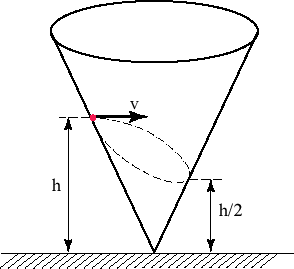
23. Difficulty: Hard 
A small ball moves without friction inside a cone with a vertical symmetry axis (see the Figure). Initially, the ball was at the height h and its velocity was directed horizontally. In its subsequent motion the object descends to the height h/2 and then climbs back. Find the speed of the ball at the highest (Vupper) and the lowest (Vlower) points of its trajectory.
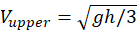
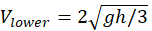
A small ball moves without friction inside a cone with a vertical symmetry axis (see the Figure). Initially, the ball was at the height h and its velocity was directed horizontally. In its subsequent motion the object descends to the height h/2 and then climbs back. Find the speed of the ball at the highest (Vupper) and the lowest (Vlower) points of its trajectory.
24. Difficulty: Expert 
A dog of mass m is standing on a boat of mass M in the lake ( m/M = 0.06 ). Both the dog and the boat are at rest. Another boat (identical to the one with the dog) is floating nearby with the velocity V0 (see the Figure). The dog jumps from her boat on the moving one and then jumps back to her boat. Assume that when leaving a boat the dog does not have any velocity relative to it. After such a maneuver, the dog's boat starts to move (the dog brought some momentum from the moving boat). The dog repeats her "trip" to another boat thus increasing the speed of her boat. What is the minimum number of such "two-way trips" the dog has to make to have her boat moving with the speed of at least V0/3? Assume there is no friction between the boats and the water.
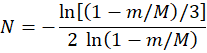
for m/M=0.06 N = 10
A dog of mass m is standing on a boat of mass M in the lake ( m/M = 0.06 ). Both the dog and the boat are at rest. Another boat (identical to the one with the dog) is floating nearby with the velocity V0 (see the Figure). The dog jumps from her boat on the moving one and then jumps back to her boat. Assume that when leaving a boat the dog does not have any velocity relative to it. After such a maneuver, the dog's boat starts to move (the dog brought some momentum from the moving boat). The dog repeats her "trip" to another boat thus increasing the speed of her boat. What is the minimum number of such "two-way trips" the dog has to make to have her boat moving with the speed of at least V0/3? Assume there is no friction between the boats and the water.
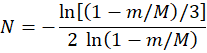
for m/M=0.06 N = 10
25. Difficulty: Expert 
A cycloid is a curve traced by a point on the rim of a circular wheel as the wheel rolls along a straight line without slippage. An object is placed on the incline having a profile of an inverted cycloid (see the Figure). Show that the time of the descent of this object without friction to the lowest point does not depend on the object’s initial position. Find the time of such descent. Express your answer in terms of the diameter of the generating wheel D, and the acceleration due to gravity g. This is a so-called tautochrone problem.
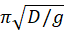
A cycloid is a curve traced by a point on the rim of a circular wheel as the wheel rolls along a straight line without slippage. An object is placed on the incline having a profile of an inverted cycloid (see the Figure). Show that the time of the descent of this object without friction to the lowest point does not depend on the object’s initial position. Find the time of such descent. Express your answer in terms of the diameter of the generating wheel D, and the acceleration due to gravity g. This is a so-called tautochrone problem.
26. Difficulty: Expert 
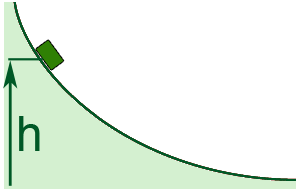
An object, initially at rest on the top of the fixed sphere, is starting to slide down without friction. Find the angle with respect to the vertical direction (see the Figure), where the object will fly off the sphere (i.e. lose contact with the sphere).
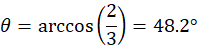
An object, initially at rest on the top of the fixed sphere, is starting to slide down without friction. Find the angle with respect to the vertical direction (see the Figure), where the object will fly off the sphere (i.e. lose contact with the sphere).
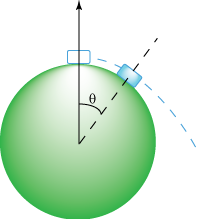
27. Difficulty: Expert 
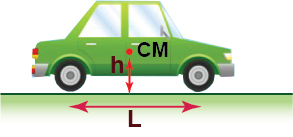
The center of mass of the car is located midway between its front and rear axles at the height h = 0.4m above ground.
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the ground is μ = 0.8. The distance between the vehicle’s axles is L = 5h (see Figure 1).
The spring constants of all 4 springs in the car’s suspension system are the same and such that for the car at rest the compression of each spring is δ = 10cm.
The car noses down during emergency braking (as it skids along the road). What is the tilt angle θ of the car during such braking (see Figure 2)?
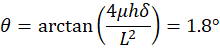
The center of mass of the car is located midway between its front and rear axles at the height h = 0.4m above ground.
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the ground is μ = 0.8. The distance between the vehicle’s axles is L = 5h (see Figure 1).
The spring constants of all 4 springs in the car’s suspension system are the same and such that for the car at rest the compression of each spring is δ = 10cm.
The car noses down during emergency braking (as it skids along the road). What is the tilt angle θ of the car during such braking (see Figure 2)?
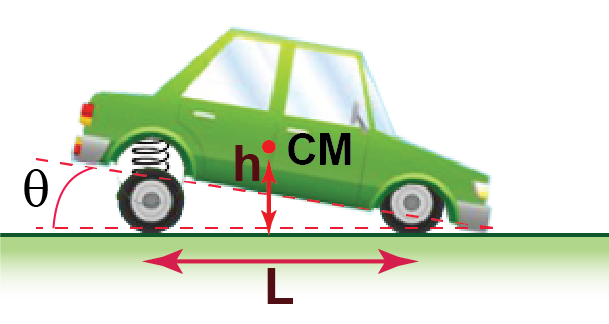
28. Difficulty: Expert 
As the car of mass M = 1200kg moves along a level road at constant speed v = 50km/h its engine produces power Plevel = 15.0kW .
This car is capable of maintaining the same constant speed along the similarly paved road inclined at the angle θ = 16° with horizontal (Figure 2). What is the power Pincline delivered by the car’s engine as the car moves up the incline?
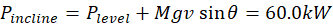
As the car of mass M = 1200kg moves along a level road at constant speed v = 50km/h its engine produces power Plevel = 15.0kW .
This car is capable of maintaining the same constant speed along the similarly paved road inclined at the angle θ = 16° with horizontal (Figure 2). What is the power Pincline delivered by the car’s engine as the car moves up the incline?
29. Difficulty: Expert 
As the car performs emergency braking from a certain initial velocity with all four wheels locked the braking distance is D. Find the braking distance (in terms of D) for the same car with the same initial speed when the car
(a) brakes with only front wheels
(b) brakes with only rear wheels.
Thr coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the ground is μ = 0.8. The center of mass of the car is located midway between its front and rear axles at the height h above ground. The distance between the vehicle’s axles is L = 4h (see the Figure).
As the car performs emergency braking from a certain initial velocity with all four wheels locked the braking distance is D. Find the braking distance (in terms of D) for the same car with the same initial speed when the car
(a) brakes with only front wheels
(b) brakes with only rear wheels.
Thr coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the ground is μ = 0.8. The center of mass of the car is located midway between its front and rear axles at the height h above ground. The distance between the vehicle’s axles is L = 4h (see the Figure).
(a) Dfront = 1.6D
(b) Drear = 2.4D
(b) Drear = 2.4D

30. Difficulty: Expert 
A hockey puck falls on the ice at the speed V0 at angle θ with horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction μ between the puck and ice does not depend on the normal force on the puck and its speed. Find the speed of the puck on the ice as a function of time.
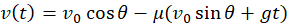
A hockey puck falls on the ice at the speed V0 at angle θ with horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction μ between the puck and ice does not depend on the normal force on the puck and its speed. Find the speed of the puck on the ice as a function of time.

31. Difficulty: Expert 
A very small ball of mass m moves in a free space with velocity V. The ball flies into the spiral labyrinth floating in space (see the Figure). The ball ends up at the center of the labyrinth. Find the angular velocity of the labyrinth once the ball is in its center. The mass of the labyrinth is M, its radius is R and its moment of inertia is I. Disregard the size of the ball.
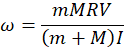
A very small ball of mass m moves in a free space with velocity V. The ball flies into the spiral labyrinth floating in space (see the Figure). The ball ends up at the center of the labyrinth. Find the angular velocity of the labyrinth once the ball is in its center. The mass of the labyrinth is M, its radius is R and its moment of inertia is I. Disregard the size of the ball.
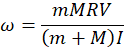
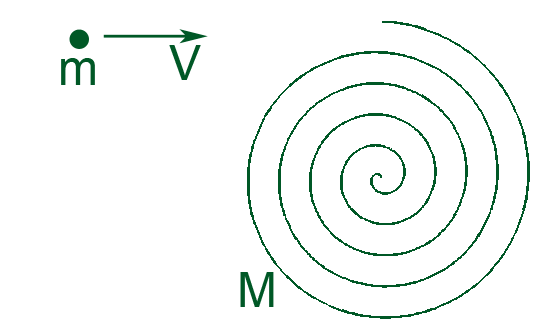
32. Difficulty: Expert 
Meteorite cloud from very far away moves towards Earth with the speed V=5 km/s. The cloud is very wide, and its depth is L = 1000km (see the Figure). The average concentration of meteorites in the cloud is n = 0.1/km3. The center of the cloud moves towards the center of Earth. Earth’s radius is R = 6378 km. Find the total number of meteorites N that will hit the Earth.
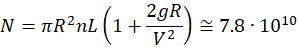
Meteorite cloud from very far away moves towards Earth with the speed V=5 km/s. The cloud is very wide, and its depth is L = 1000km (see the Figure). The average concentration of meteorites in the cloud is n = 0.1/km3. The center of the cloud moves towards the center of Earth. Earth’s radius is R = 6378 km. Find the total number of meteorites N that will hit the Earth.

33. Difficulty: Expert 
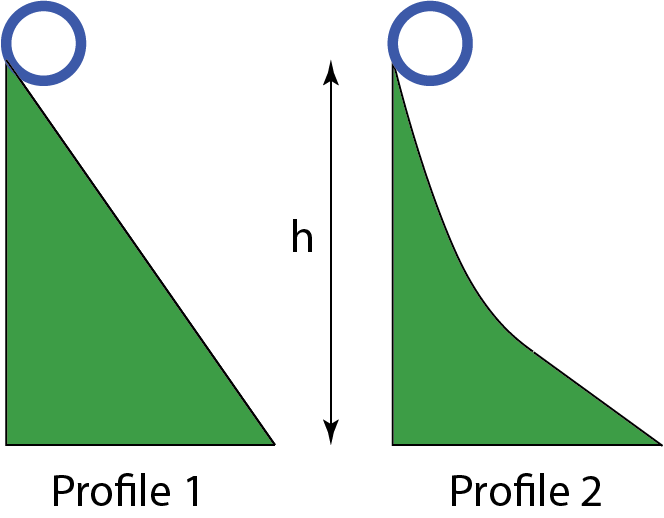
A massive hollow cylinder rolls down two inclines with the same heights but different profiles (see the Figure). The cylinder rolls down an incline with profile 1 without slipping while there is some slipping as the cylinder rolls down an incline with profile 2. For which profile the final speed of the cylinder at the bottom of the incline is greater?
A massive hollow cylinder rolls down two inclines with the same heights but different profiles (see the Figure). The cylinder rolls down an incline with profile 1 without slipping while there is some slipping as the cylinder rolls down an incline with profile 2. For which profile the final speed of the cylinder at the bottom of the incline is greater?
the speed is greater at the bottom of the incline with profile 1. For profile 2 some energy is lost on kinetic friction due to slipping therefore kinetic energy at the bottom is less than for profile 1.
34. Difficulty: Expert 
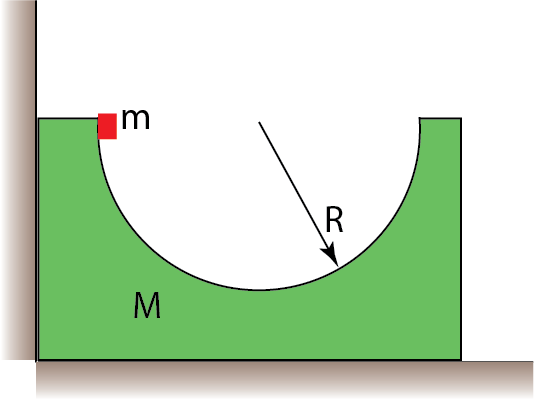
A block of mass M has a semispherical cavity of radius R (see the Figure). The block rests on a frictionless surface adjacent to the wall. A small nut of mass m is placed in the spherical cavity close to its top adjacent to the wall (see the Figure). The nut is released from rest and slides down the cavity without friction. The system starts to move. Find the maximum speed of the block.
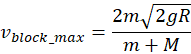
A block of mass M has a semispherical cavity of radius R (see the Figure). The block rests on a frictionless surface adjacent to the wall. A small nut of mass m is placed in the spherical cavity close to its top adjacent to the wall (see the Figure). The nut is released from rest and slides down the cavity without friction. The system starts to move. Find the maximum speed of the block.
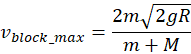
35. Difficulty: Expert 
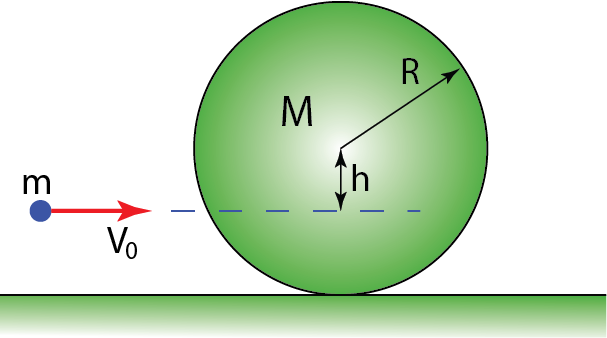
A bullet with mass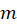 moving horizontally with velocity V0 hits a solid sphere at rest on a rough surface. The mass of the sphere is
moving horizontally with velocity V0 hits a solid sphere at rest on a rough surface. The mass of the sphere is 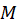 , and its radius is R. The bullet hits the sphere at a distance h below the center of the sphere and gets embedded there (see the Figure). Find the speed of the sphere once it rolls without slipping on the horizontal surface. Assume
, and its radius is R. The bullet hits the sphere at a distance h below the center of the sphere and gets embedded there (see the Figure). Find the speed of the sphere once it rolls without slipping on the horizontal surface. Assume 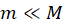 .
.
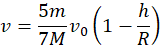
A bullet with mass
© Copyright Angas Tutoring. All Rights Reserved.